The amount of data that may be transported from one point to another inside a network in a given amount of time is referred to as bandwidth. Typically, bandwidth is measured in bits per second and expressed as a bitrate (bps).
The term bandwidth refers to a connection’s transmission capacity. It is an important aspect in evaluating a network’s or internet connection’s quality and speed.
There are various methods for determining it. Some metrics are used to calculate current data flow.
The concept of bandwidth is also important in a variety of other technological domains. It is commonly measured in hertz in signal processing and describes the difference between the upper and lower frequencies in a transmission such as a radio signal (Hz).
This is comparable to the flow of water via a conduit. The pace at which water (data) flows through the pipe (connection) under varied conditions is as bandwidth. We could measure liters per minute instead of bits per second.
Originally, it measured in bits per second and expressed as bps.
However, today’s networks often have much more capacity than such small units can comfortably convey.
Higher figures with metric prefixes, such as Mbps (megabits per second), Gbps (gigabits per second), or Tbps (terabits per second), are already popular (terabits per second).
K = kilo = 1,000 bits
M = mega = 1,000 kilo = 1,000,000 bits
G = giga = 1,000 mega = 1,000,000,000 bits
T = tera = 1,000 giga = 1,000,000,000,000 bits

After terabit, there are petabit, exabit, zettabit, and yottabit, each representing an additional power of 10.
Measuring bandwidth
On an IP network between two hosts, TTCP measures throughput.
The recipient is one host, and the sender is the other.
The number of bytes transmitted and the time it takes for each packet to complete the one-way trip are displayed on both sides.
PRTG has a graphical interface and charts for measuring bandwidth trends over extended periods of time. As well as the ability to measure traffic across many interfaces.
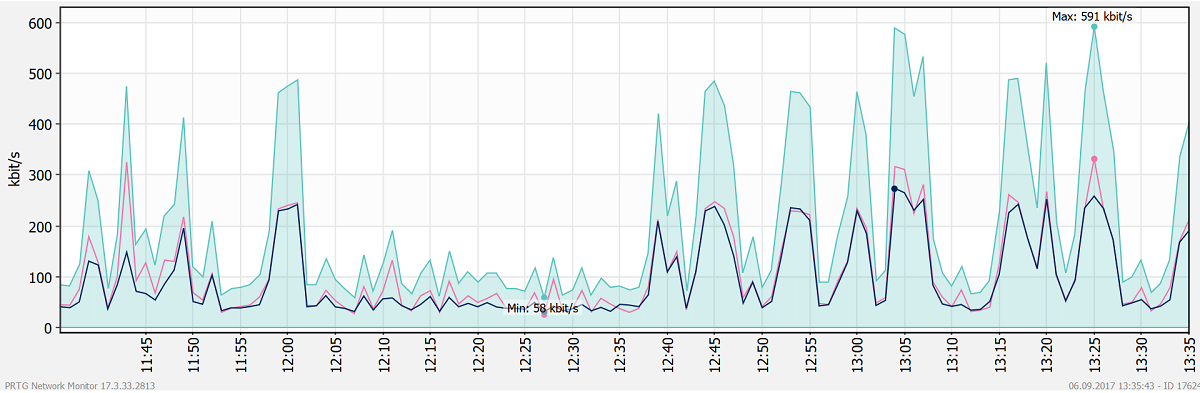
Another way to determine it is to transmit a file (or several files) of known size and time how long it takes to complete the transfer. The result is translated to bits per second (bps) by dividing the file size by the amount of time the transfer took.
Most internet speed tests use this method to determine how fast a user’s computer connects to the internet.
While there is no way to measure entire available bandwidth, measurable bandwidth can be in a variety of ways, depending on the need.
Bandwidth vs. speed vs. throughput
There are numerous approaches to considering data flow in a network. The bit rate of the circuit determines the network’s speed.
The amount of physical circuit capacity that can transport data defines by the amount of network capacity that is available based on the connection.
While a Gigabit Ethernet network connection allows for 1 Gbps, a PC connected via a Fast Ethernet card only has 100 Mbps of bandwidth.
Throughput refers to the rate at which data successfully transmits. Whereas bandwidth refers to the amount of data that travels through the network interface regardless of whether the data successfully transmits.
As a result, throughput always falls short of bandwidth.
Low usable this compares to theoretical maximum bandwidth may indicate network issues. Especially if various areas of a network that operate in the same way have vastly varying usable bandwidths.
Users at home can perform an online bandwidth test like the DSLReports speed test to discover how much of the “up to 40 Mb/s” connection their internet service provider (ISP) charges them for is actually useful.
Measuring throughput between offices connected by a carrier-leased line connection may be a better option for corporate connections.
Bandwidth issues
Despite the fact that current protocols are rather effective at not dropping packets, restricted bandwidth can still cause operations to take too long to finish.
These vulnerabilities can result in database or application faults.
When backing up or transferring data across a network, insufficient bandwidth might cause backups to take too long, disrupting other batch activities or even interrupting normal business hours.
Users attempting to make phone calls over a network will experience worse call quality if they have insufficient bandwidth. Based on the available bandwidth, most VoIP systems degrade the fidelity of a connection. The call may sound “tinny” or “echo-y” if there isn’t enough bandwidth.
If the call quality is poor enough, there may be pauses in the dialogue where parts of the chat are lost.
Even more bandwidth is must-have for video calls. Video calls with insufficient bandwidth will result in poor voice quality as well as low-quality or choppy video.
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) of the United States recommends a minimum bandwidth of 4 Mbps for adequate performance when streaming a video in HD resolution.
Many video players will “buffer,” or download data before it presents, in order to use less bandwidth.
If the connection is too slow, users may have to wait a long time for the video to start while the system buffers a large amount of data. Or the video may abruptly end when the system runs out of buffered video to play.
Click here to read more useful and interesting articles.


